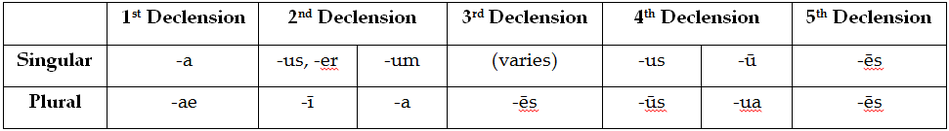
NOMINATIVE CASE - WHAT IT LOOKS LIKE
The nominative case is the most basic version of a noun, and it's probably the first one you'll ever see when you learn that noun. It only has a couple uses, but those uses are super-important and fundamental to the Latin language. Here are the endings for the different declensions:
NOMINATIVE CASE - WHAT IT'S USED FOR
Subject
The most common use of the nominative is the most basic function a noun can have: the subject of a sentence, the person or thing doing the main action.
Caecilius slaps Quintus. The cow jumped over the moon. The gladiator is afraid.
Caecilius Quintum depalmat. vacca super lunā saluit. gladiator timet.
Predicate Nominative
You also use the nominative in the predicate if it is renaming or re-describing the subject, following a form of the verb “be” – in other words, if you’re just saying it IS the same thing as the subject.
Caecilius is a banker. Cleopatra was queen of Egypt.
Caecilius est argentarius. Cleopatra erat regina Aegypti.
The most common use of the nominative is the most basic function a noun can have: the subject of a sentence, the person or thing doing the main action.
Caecilius slaps Quintus. The cow jumped over the moon. The gladiator is afraid.
Caecilius Quintum depalmat. vacca super lunā saluit. gladiator timet.
Predicate Nominative
You also use the nominative in the predicate if it is renaming or re-describing the subject, following a form of the verb “be” – in other words, if you’re just saying it IS the same thing as the subject.
Caecilius is a banker. Cleopatra was queen of Egypt.
Caecilius est argentarius. Cleopatra erat regina Aegypti.
VOCATIVE CASE - WHAT IT LOOKS LIKE
The vocative case looks exactly the same as the nominative in all cases EXCEPT for nouns in the second declension. 2nd declension nouns that end in “-us” in the nominative will end in “-e” in the vocative. 2nd declension nouns that end in “-ius” in nominative will end in “-ī” in the vocative.
VOCATIVE CASE - WHAT IT'S USED FOR
The vocative is the case you use when you are speaking directly to someone, whether talking to them by name or calling them something other than their name.
Examples:
Rufilla, how are you feeling today? Maximus, kill the gladiator! Salvius, you are stupid.
Rufilla, quo modo sentis hodie? Maxime, neca gladiatorem! Salvī, stultus es.
American woman, get away from me. Banker, give me money. Slave, you ought to work.
femina Americana, linque me. argentarī, da mihi pecuniam. serve, tu laborare debes.
Examples:
Rufilla, how are you feeling today? Maximus, kill the gladiator! Salvius, you are stupid.
Rufilla, quo modo sentis hodie? Maxime, neca gladiatorem! Salvī, stultus es.
American woman, get away from me. Banker, give me money. Slave, you ought to work.
femina Americana, linque me. argentarī, da mihi pecuniam. serve, tu laborare debes.